给定一张 $n$ 个点的图,完成 $q$ 次建边操作,每次建边有权值:
- 建有向边 $v\rightarrow u$。
- 对于 $i\in[l,r]$,建边 $v\rightarrow i$。
- 对于 $i\in[l,r]$,建边 $i\rightarrow v$。
求最终图的最短路。
满足 $1\leq n\leq10^5$。
线段树优化建图
朴素建图会产生至多 $\mathcal O(qn)$ 条边,这是无法接受的。
区间操作,考虑使用线段树如何去优化这个过程。
例如,$n=4$,对于 $i\in[1,3]$,建边 $4\rightarrow i$。
如果有一个虚拟节点 $[1,2]$ 向 $1,2$ 均连了权值为 $0$ 的边,那么等价于建边 $4\rightarrow[1,2],4\rightarrow3$:
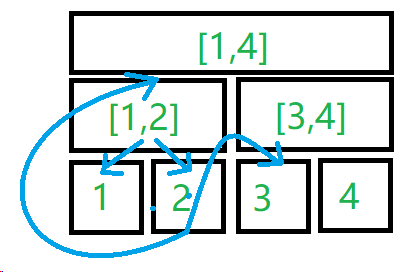
这是一棵维护 $x\rightarrow[l,r]$ 的线段树,同样还有一棵维护 $x\leftarrow[l,r]$ 的线段树。
这样,单次操作至多增加 $\mathcal O(\log n)$ 条边,复杂度可以接受。
网络上有很多两棵线段树间连边的图,然而这样是完全没必要的。钦定线段树叶节点对应原图对应节点即可。
这样,只需要 $\mathcal O(3n)$ 个节点和 $\mathcal O(q\log n)$ 条边,就可以解决原问题。
注意「线段树优化建图」中的线段树不需要维护除对应原图节点、区间端点编号外的任何信息,仅仅是为了建图。
例题 AC 代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
constexpr const int N=1e5;
constexpr const ll inf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f;
int n,cnt;
vector<pair<int,ll> >g[N<<3|1];
struct segTree{
bool mode;
struct node{
int l,r;
int id;//图上编号
}t[N<<2|1];
void build0(int p,int l,int r){
t[p]={l,r};
if(l==r){
t[p].id=l;
return;
}
t[p].id=++cnt;
int mid=l+r>>1;
build0(p<<1,l,mid);
build0(p<<1|1,mid+1,r);
if(!mode){
g[t[p].id].push_back({t[p<<1].id,0});
g[t[p].id].push_back({t[p<<1|1].id,0});
}else{
g[t[p<<1].id].push_back({t[p].id,0});
g[t[p<<1|1].id].push_back({t[p].id,0});
}
}
void build(int l,int r,bool Mode){
mode=Mode;
build0(1,l,r);
}
//mode=0:x -> [l,r]
//mode=1:x <- [l,r]
void create(int p,int l,int r,int x,int w){
if(l<=t[p].l&&t[p].r<=r){
if(!mode){
g[x].push_back({t[p].id,w});
}else{
g[t[p].id].push_back({x,w});
}
return;
}
if(l<=t[p<<1].r){
create(p<<1,l,r,x,w);
}
if(t[p<<1|1].l<=r){
create(p<<1|1,l,r,x,w);
}
}
}A,B;
ll dis[N<<3|1];
void Dijkstra(int s){
priority_queue<pair<ll,int>,vector<pair<ll,int> >,greater<pair<ll,int> > >q;
memset(dis,0x3f,sizeof(dis));
static bool vis[N<<3|1];
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
dis[s]=0;
q.push({dis[s],s});
while(q.size()){
int x=q.top().second;q.pop();
if(vis[x]){
continue;
}
vis[x]=true;
for(auto &i:g[x]){
int &v=i.first;
ll &w=i.second;
if(vis[v]){
continue;
}
if(dis[x]+w<dis[v]){
dis[v]=dis[x]+w;
q.push({dis[v],v});
}
}
}
}
int main(){
/*freopen("test.in","r",stdin);
freopen("test.out","w",stdout);*/
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int q,s;
cin>>n>>q>>s;
cnt=n;
A.build(1,n,0);
B.build(1,n,1);
while(q--){
int op,u,v,l,r,w;
cin>>op>>v;
switch(op){
case 1:
cin>>u>>w;
g[v].push_back({u,w});
break;
case 2:
cin>>l>>r>>w;
A.create(1,l,r,v,w);
break;
case 3:
cin>>l>>r>>w;
B.create(1,l,r,v,w);
break;
}
}
Dijkstra(s);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(dis[i]==inf){
cout<<"-1 ";
}else{
cout<<dis[i]<<' ';
}
}
cout.flush();
/*fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);*/
return 0;
}