其实和[集训队互测 2011] Crash 的文明世界是差不多的。
题意分析
树上问题
首先,$n$ 个点 $n-1$ 条边,显然是一个树。
设 $\operatorname{dist}(i,j)$ 表示以 $i$ 为根节点时,$j$ 的深度。不难发现这其实就是任意节点为根节点时,$i,j$ 之间的树上距离加 $1$。因此令 $\operatorname{dist}(i,j)$ 表示 $i,j$ 之间的距离。
斯特林数
对于整数 $x$ 的 $k$ 次方,其实可以通过第二类斯特林数展开:
\[\begin{aligned} x^k&=\sum_{i=0}^k\begin{Bmatrix}k\\i\end{Bmatrix}x^{\underline{i}}\\ &=\sum_{i=0}^k\begin{Bmatrix}k\\i\end{Bmatrix}i!\dbinom{x}{i}\\ \end{aligned}\]因此,$S(u)$ 就可以转化为:
\[\begin{aligned} S(u)&=\sum_{v=1}^n(\operatorname{dist}(u,v)+1)^k\\ &=\sum_{v=1}^n\sum_{i=0}^k\begin{Bmatrix}k\\i\end{Bmatrix}i!\dbinom{\operatorname{dist}(u,v)+1}{i}\\ &=\sum_{i=0}^k\begin{Bmatrix}k\\i\end{Bmatrix}i!\sum_{v=1}^n\dbinom{\operatorname{dist}(u,v)+1}{i} \end{aligned}\]树形 DP
不难发现,关键便在于对于每一个点 $u$,求出 $\sum\limits_{v=1}^n\dbinom{\operatorname{dist}(u,v)+1}{i}$,且 $0\leq i\leq k$。
如果 $u$ 确定,其实很简单,只需要 DFS 一遍即可。但是需要对于每一个点 $u$ 都求一次,暴力 DFS 的复杂度是 $\mathcal O\left(n^2\right)$ 的,无法接受。
不难发现,设边 $(x,y)$,且 $x$ 为 $y$ 的父节点,则将树根从 $x$ 变为 $y$ 是会且仅会影响 $x,y$ 的答案的。因此考虑换根 DP。
第一次 DP
设 $\textit{dp}{x,i}$ 表示节点 $x$ 的子树内,$i=i$ 时的 $\sum\limits{y=1}^n\dbinom{\operatorname{dist}(x,y)+1}{i}$。
记 $\textit{son}_x$ 表示 $x$ 的子节点集。
显然,有:
\[\begin{aligned} \textit{dp}_{x,0}&=\sum_{y\in\textit{son}_x}\textit{dp}_{y,0}+1\\ \textit{dp}_{x,1}&=\sum_{y\in\textit{son}_x}(\textit{dp}_{y,1}+\textit{dp}_{y,0})+1\\ \textit{dp}_{x,i}&=\sum_{y\in\textit{son}_x}\left(\textit{dp}_{y,i}+\textit{dp}_{y,i-1}\right) \end{aligned}\]-
$i=0$ 时,无论 $\operatorname{dist}(x,y)$ 取何值,总有 $\dbinom{\operatorname{dist}(x,y)+1}{0}=1$。因此,$\textit{dp}_{x,0}$ 就是 $x$ 子树内节点个数,包括自己。
-
$i=1$ 时,$\dbinom{\operatorname{dist}(x,x)+1}{0}=1$。
-
$i\neq0$ 时,考虑组合数递推公式:
\[\dbinom{\operatorname{dist}(x,y)+1}{i}=\dbinom{\operatorname{dist}(x,y)}{i}+\dbinom{\operatorname{dist}(x,y)}{i-1}\]$\operatorname{dist}(x,y)-1$,即对应从 $y$ 开始。因为 $y$ 对应的是 $y$ 的子树中的贡献,$x$ 走进去必然经过长度为 $1$ 的 $(x,y)$。
故,有:
\[\textit{dp}_{x,i}=\textit{dp}_{y,i}+\textit{dp}_{y,i-1}\]
换根 DP
设根节点 $x$ 为 $y$ 的父节点,已知 $\textit{dp}{x,i}$,推出 $y$ 为根节点时的 $\textit{dp}{y,i}$。
如图:
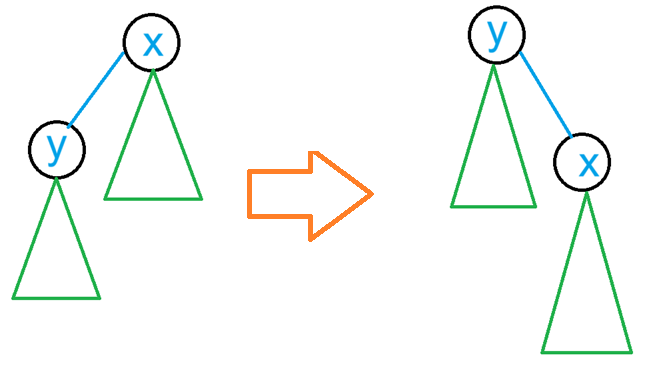
首先,要求出 $x$ 作为根节点 $y$ 的子节点时的子树内的 $\textit{dp}’_{x,i}$。
只需要减去 $y$ 对 $x$ 的贡献即可。
即:
\[\begin{aligned} \textit{dp}'_{x,0}&=\textit{dp}_{x,0}-\textit{dp}_{y,0}\\ \textit{dp}'_{x,i}&=\textit{dp}_{x,i}-(\textit{dp}_{y,i}+\textit{dp}_{y,i-1}) \end{aligned}\]这时,想求出根节点 $y$ 的 $\textit{dp}’{y,i}$,只需要加上对应的 $\textit{dp}’{x,i}$ 即可:
\[\begin{aligned} \textit{dp}'_{y,0}&=\textit{dp}_{y,0}+\textit{dp}'_{x,0}\\ \textit{dp}'_{y,i}&=\textit{dp}_{y,i}+(\textit{dp}'_{x,i}+\textit{dp}'_{x,i-1}) \end{aligned}\]这样,我们就将根节点从 $x$ 换成了 $y$,这时 $\mathcal O(k)$ 统计答案即可。
AC 代码
注意答案非负。
时间复杂度:$\mathcal O\left(Tnk\right)$。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
constexpr const int N=20000,K=20,P=1e9+7;
int n,k,ans[N+1];
vector<int>g[N+1];
namespace base{
int qpow(int base,int n){
int ans=1;
while(n){
if(n&1){
ans=1ll*ans*base%P;
}
base=1ll*base*base%P;
n>>=1;
}
return ans;
}
int fact[K+1];
void pre(){
fact[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=K;i++){
fact[i]=1ll*fact[i-1]*i%P;
}
}
int C(int n,int m){
if(n<0||m<0||n<m){
return 0;
}
static int mem[N+1][K+1];
if(!m){
return 1;
}
if(mem[n][m]){
return mem[n][m];
}
return mem[n][m]=C(n-1,m)+C(n-1,m-1);
}
int Stirling2(int n,int k){
static int mem[K+1][K+1];
if(n<0||k<0||n<k){
return 0;
}
if(!k){
return !n;
}
if(mem[n][k]){
return mem[n][k];
}
return mem[n][k]=(Stirling2(n-1,k-1)+1ll*k*Stirling2(n-1,k)%P)%P;
}
}
namespace DP{
int dp[N+1][K+1];
void dfs0(int x,int fx){
dp[x][0]=dp[x][1]=1;
for(int y:g[x]){
if(y==fx){
continue;
}
dfs0(y,x);
dp[x][0]=(1ll*dp[x][0]+dp[y][0])%P;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){
dp[x][i]=(1ll*dp[x][i]+dp[y][i]+dp[y][i-1])%P;
}
}
}
void dfs1(int x,int fx){
ans[x]=0;
for(int i=0;i<=k;i++){
ans[x]=(1ll*ans[x]+1ll*dp[x][i]*base::Stirling2(k,i)%P*base::fact[i]%P)%P;
if(ans[x]<0){
ans[x]+=P;
}
}
for(int y:g[x]){
if(y==fx){
continue;
}
dp[x][0]=(dp[x][0]-dp[y][0])%P;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){
dp[x][i]=(dp[x][i]-dp[y][i]-dp[y][i-1])%P;
}
dp[y][0]=(dp[y][0]+dp[x][0])%P;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){
dp[y][i]=(dp[y][i]+dp[x][i]+dp[x][i-1])%P;
}
dfs1(y,x);
dp[y][0]=(dp[y][0]-dp[x][0])%P;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){
dp[y][i]=(dp[y][i]-dp[x][i]-dp[x][i-1])%P;
}
dp[x][0]=(dp[x][0]+dp[y][0])%P;
for(int i=1;i<=k;i++){
dp[x][i]=(dp[x][i]+dp[y][i]+dp[y][i-1])%P;
}
}
}
int main(){
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
dfs0(1,0);
dfs1(1,0);
return 0;
}
}
main(){
/*freopen("test.in","r",stdin);
freopen("test.out","w",stdout);*/
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
int T;
cin>>T;
while(T--){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
g[i].resize(0);
}
cin>>n>>k;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
int u,v;
cin>>u>>v;
u++,v++;
g[u].push_back(v);
g[v].push_back(u);
}
base::pre();
DP::main();
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cout<<ans[i]<<'\n';
}
cout<<'\n';
}
cout.flush();
/*fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);*/
return 0;
}