边双连通分量
众所周知,在有向图中,存在强连通分量,强连通分量中的任意两点是连通的。
而在无向图中,同样存在边双连通分量。
边双连通
若一个无向连通图删去任意一条边之后仍然连通,则该图边双连通。
边双连通分量
在满足边双连通的前提下尽可能大的子图。
Tarjan 求边双连通分量
前置知识:Tarjan 求强连通分量
Tarjan 求边双连通分量
把求有向图强连通分量的代码拿过来改改就行了,
无向图转有向图存储下环的误判
具体而言,就是不能出现如图的情况:

$x,y$ 之间只有一条边,不是环,然而如果转换为有向图存储:

就存在了环。
因此我们需要防止其重复走,因此我们可以给边标号。
但是这样其实不是最优的,有一种更好的方式:邻接表存储边时,从 $2$ 号开始存储,并且无向边转换为的两条有向边相邻存储。
这样的好处就是,比如说 $x$ 号边是代表 $u\to v$ 的,那么 $x\oplus 1$ 号边代表的就是 $v\to u$ 的,其中 $\oplus$ 表示异或。
前向边与横边不存在
一棵有向图的 DFS 生成树如图:
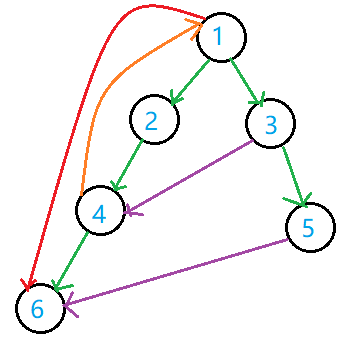
图中绿色为普通树边,橙色为回溯边,红色为前向边,紫色为横边。
考虑到无向图,实际上 DFS 生成树中只有普通树边和回溯边。
-
前向边不存在,因为无向,因此前向边反向就是一条回溯边。
-
横边不存在,因为按照 DFS 搜索顺序不会使其有可能存在。
例如图中搜索到 $4$ 之后,按照 DFS 的原则会先后搜索 $3,6$,不可能只搜索 $6$ 然后回退至 $1$ 再搜索到 $3$,然后连横边。
即化为:
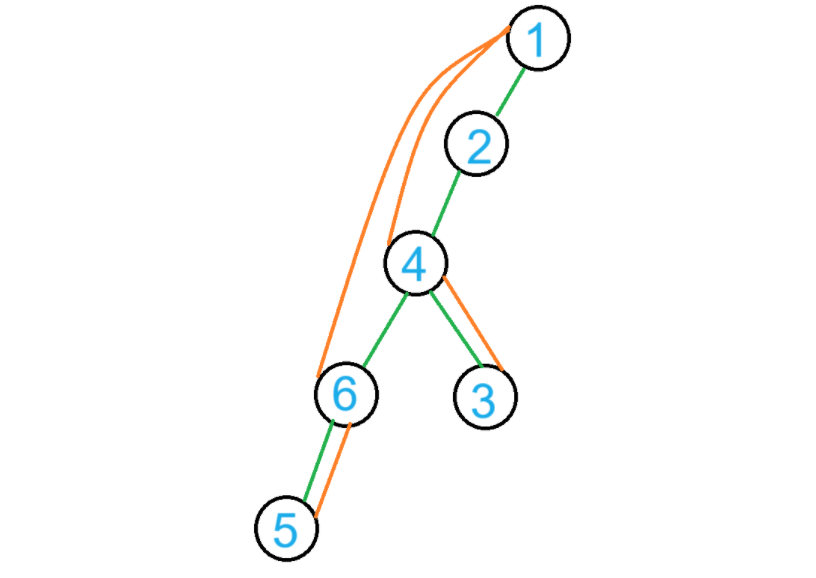
也就是说,我们不再需要判断元素是否在栈中(判断了也能过),更新 $low_x$ 部分的代码可以简化为:
1
2
3
4
if(!dfn[v]){
Tarjan(v,i);
low[x]=min(low[x],low[v]);
}else low[x]=min(low[x],dfn[v]);
答案存储
使用 vector 即可。
但是不建议使用 vector 套 vector,即类似:
1
vector<vector<int> >ans;
因为这样效率低下。
建议改为:
1
2
int ansSize;
vector<int>ans[N];
AC 代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
//#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
constexpr const int N=5e5,M=2e6;
struct graph{
struct edge{
int v,r;
}a[2*M+1];
int h[N+1];
void create(int u,int v){
static int top=1;
a[++top]={v,h[u]};
h[u]=top;
}
}g;
int dfn[N+1];
int ansSize;
vector<int>ans[N+1];
void Tarjan(int x,int last){
static int top,s[N+1],low[N+1];
dfn[x]=low[x]=++top;
s[top]=x;
for(int i=g.h[x];i;i=g.a[i].r){
int &v=g.a[i].v;
if(i==(last^1))continue;
if(!dfn[v]){
Tarjan(v,i);
low[x]=min(low[x],low[v]);
}else low[x]=min(low[x],dfn[v]);
}
if(dfn[x]==low[x]){
ans[++ansSize].resize(0);
while(s[top]!=x){
ans[ansSize].push_back(s[top--]);
}ans[ansSize].push_back(s[top--]);
}
}
int main(){
/*freopen("test.in","r",stdin);
freopen("test.out","w",stdout);*/
int n,m;
scanf("%d %d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
int u,v;
scanf("%d %d",&u,&v);
g.create(u,v);
g.create(v,u);
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(!dfn[i])Tarjan(i,0);
}
printf("%d\n",ansSize);
for(int i=1;i<=ansSize;i++){
printf("%d",ans[i].size());
for(int &j:ans[i])printf(" %d",j);
putchar(10);
}
/*fclose(stdin);
fclose(stdout);*/
return 0;
}